[成果] 基于相似优先扩散机制的科学论文排序方法
研究成果:Jianlin Zhou, An Zeng*, Ying Fan* and Zengru Di. Ranking scientific publications with similarity-preferential Mechanism. [Scientometrics, (2015), DOI: 10.1007/s11192-015-1805-1]
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11192-015-1805-1
基于相似优先扩散机制的科学论文排序方法
摘要:
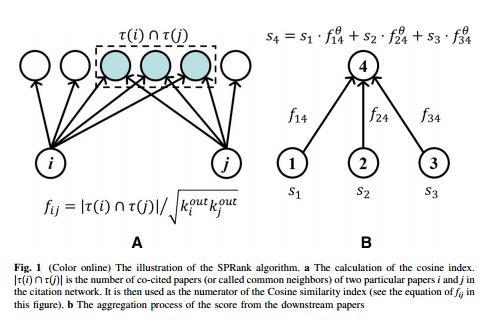
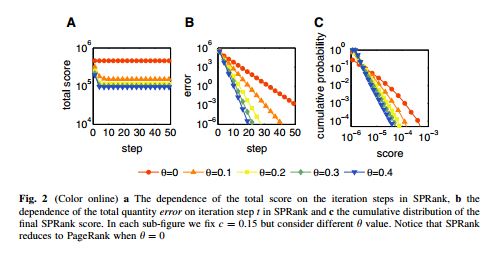
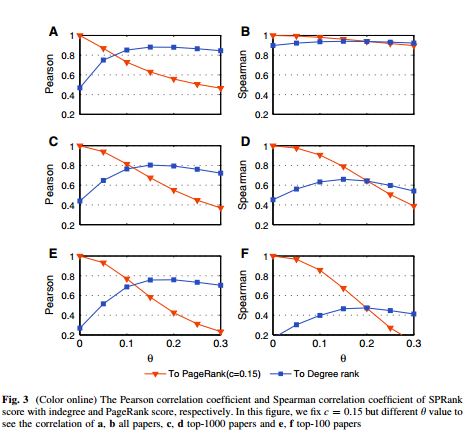
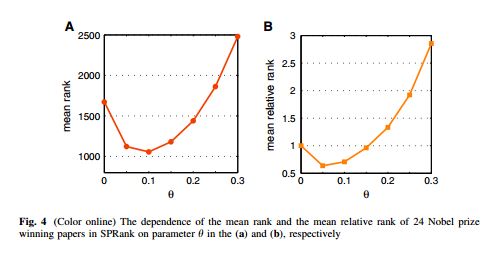
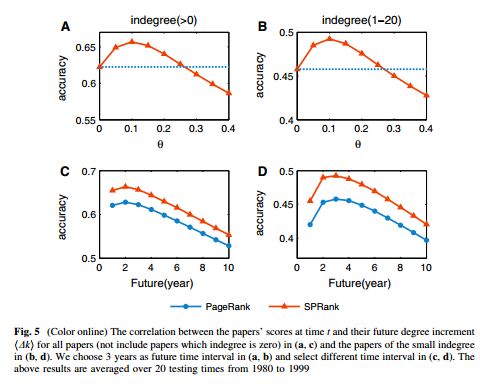
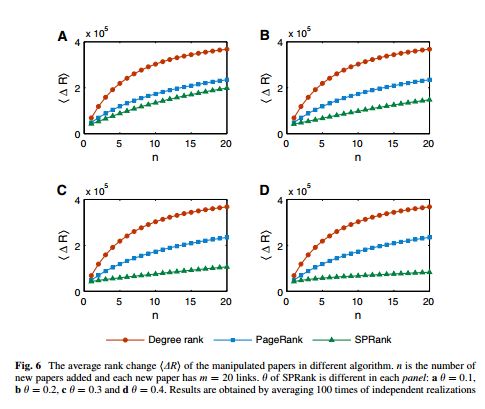
随着因特网的发展,现在研究者们越来越容易获得科学论文。然而,从大量的科学论文中发现高质量的作品不是一件容易的事情。在已有的算法中,Pagerank是比较具有代表性的一种。它源于谷歌搜索引擎的底层算法,在网络中通过迭代扩散过程为每个节点赋予一定的资源,节点的稳态资源即为它的重要程度。本文在Pagerank的基础上加入相似优先的扩散机制,即当一个节点接收下游节点扩散资源的时候,以一定程度忽略弱相似节点的资源。算法的有效性在美国物理学会引文网络上通过诺贝尔奖文章以及算法预测能力得以验证。另外,此算法对于引文中的蓄意行为有很强的鲁棒性。虽然此算法在本文中针对科学引文网设计,它可以自然的推广到网页搜索算法的设计以及社会网络中领导力的挖掘。
Abstract:
Along with the advance of internet and fast updating of information, nowadays it is much easier to search and acquire scientific publications. To identify the high quality articles from the paper ocean, many ranking algorithms have been proposed. One of these methods is the famous PageRank algorithm which was originally designed to rank web pages in online systems. In this paper, we introduce a preferential mechanism to the PageRank algorithm when aggregating resource from different nodes to enhance the effect of similar nodes. The validation of the new method is performed on the data of American Physical Society journals. The results indicate that the similarity-preferential mechanism improves the performance of the PageRank algorithm in terms of ranking effectiveness, as well as robustness against malicious manipulations. Though our method is only applied to citation networks in this paper, it can be naturally used in many other real systems, such as designing search engines in the World Wide Web and revealing the leaderships in social networks.